python机器人Agent编程——实现一个本地大模型和爬虫结合的手机号归属地天气查询Agent
一、前言
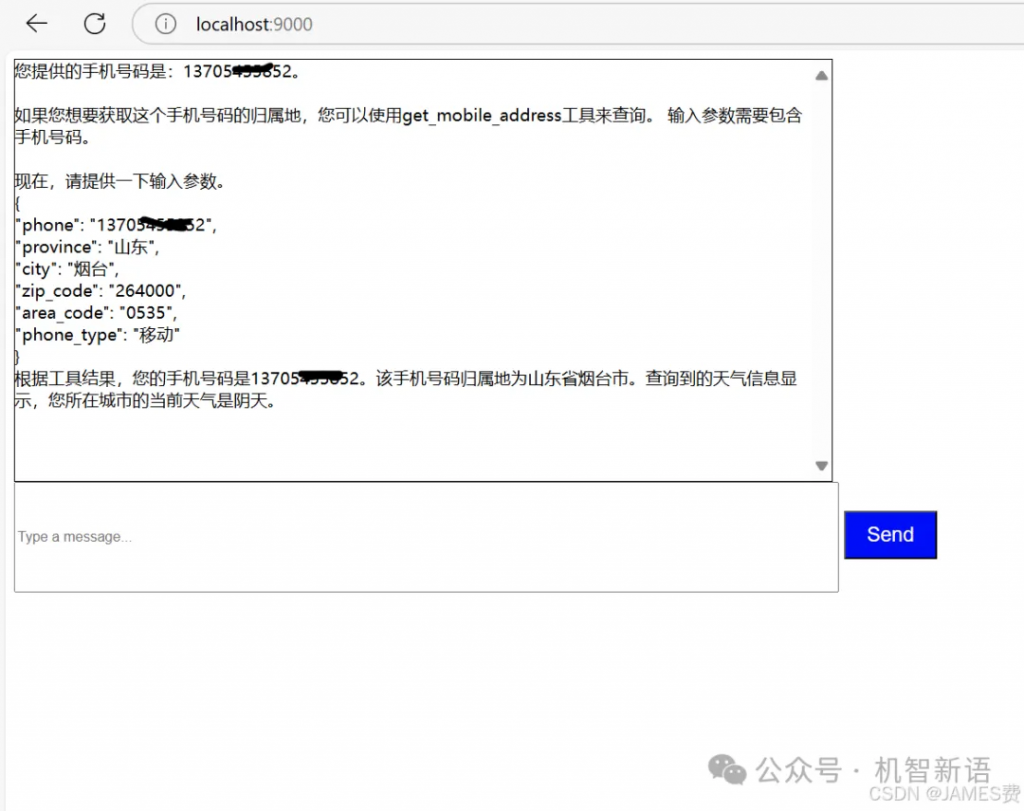
在本文中,我们将逐步实现一个手机号归属地天气查询agent。这个agent将能够接收用户的手机号输入,自动查询该手机号的归属地,并进一步根据获取的城市信息查询该地区的实时天气信息。我们将使用Python语言,并结合qwen_agent库,及fastapi服务来实现这个功能。
二、准备工作
首先,确保你已经安装了Python环境和以下库:
- qwen_agent:用于创建agent的框架。
- requests:用于发送HTTP请求。
- phone:用于查询手机号归属地
- json:用于处理JSON数据。
- re:用于正则表达式匹配。
- 本地大模型服务:ollama本地大模型管理软件及qwen大模型。
- fastapi:用户构建web前端聊天界面
如果还没有安装这些库,可以通过以下命令安装:
pip install qwen_agent requests #其它所需的模块这里如果没有装所需的库,运行时会提示,根据提示安装缺的库即可。
没有ollama也先去安装ollama并运行qwen大模型,过程非常简单,网上很多,不再赘述。

三、Agent结构
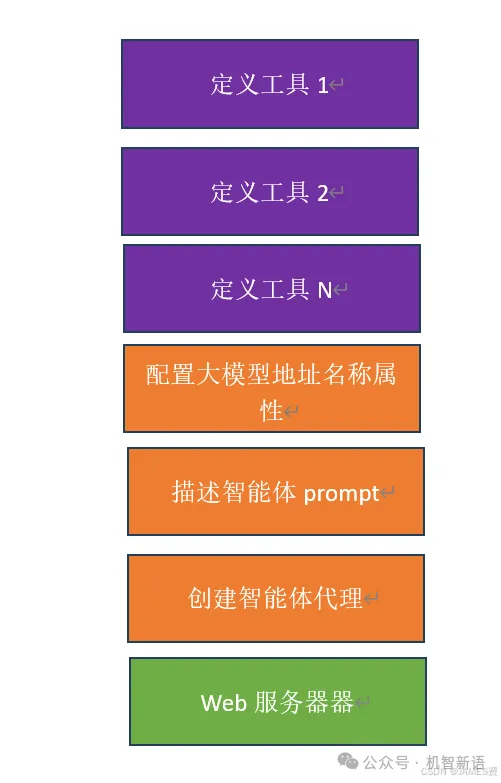
qwen智能体基本结构是这样的:先定义工具类tools,然后定义智能体的任务描述,然后创建一个智能体,再然后就是web发布智能体服务,进行双向通讯。
四、python模块实现
4.1 实现手机号归属地查询工具
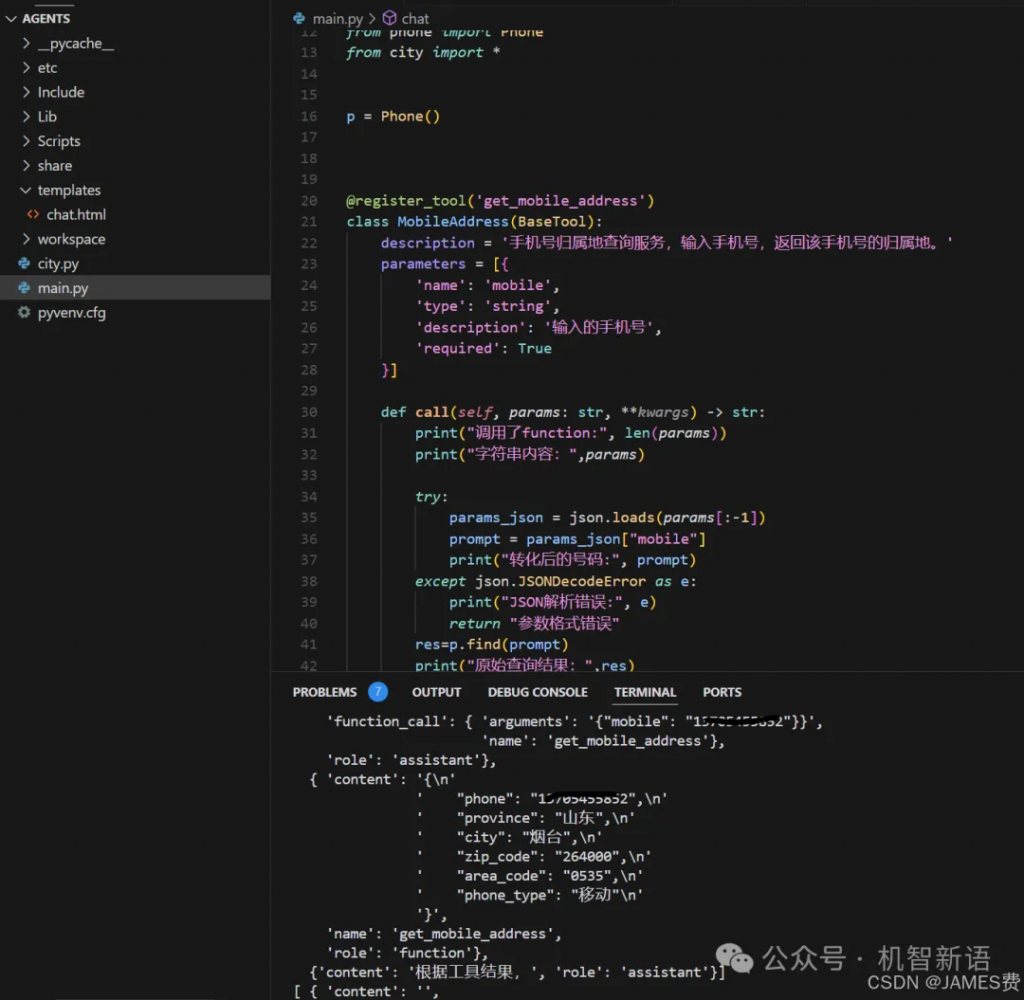
我们首先定义一个工具MobileAddress,用于查询手机号的归属地。这个工具将使用一个外部API来获取归属地信息。
@register_tool('get_mobile_address')
class MobileAddress(BaseTool):
description = '手机号归属地查询服务,输入手机号,返回该手机号的归属地。'
parameters = [{
'name': 'mobile',
'type': 'string',
'description': '输入的手机号',
'required': True
}]
def call(self, params: str, **kwargs) -> str:
print("调用了function:", len(params))
print("字符串内容:",params)
try:
params_json = json.loads(params[:-1])
prompt = params_json["mobile"]
print("转化后的号码:", prompt)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print("JSON解析错误:", e)
return "参数格式错误"
res=p.find(prompt)
print("原始查询结果:",res)
return res4.2实现天气查询工具
接下来,我们定义另一个工具WeatherByAddress,用于根据城市名称查询天气信息。这个工具将使用另一个外部API来获取天气数据。
@register_tool('get_weather')
class WeatherByAddress(BaseTool):
description = '根据提供的城市名称,查找代码,并通过互联网请求查询天气信息。'
parameters = [{'name': 'city', 'type': 'string', 'description': '城市名称', 'required': True}]
def call(self, params: str, **kwargs) -> str:
try:
params_json = json.loads(params)
city_name = params_json["city"]
# 假设我们有一个城市代码的映射字典
city_code = {'Beijing': '101010100'} # 示例代码
url = f'https://www.weather.com.cn/weather1d/{city_code[city_name]}.shtml'
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
html_content = response.text
match = re.search(r'var hour3data=(\{.*?\});', html_content)
if match:
hour3data = match.group(1)
return hour3data
else:
return "未找到天气小时数据"
else:
return "请求失败,状态码: {}".format(response.status_code)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
return "参数格式错误"4.3定义创建Agent主体
最后,我们创建一个Assistant实例,这个agent将使用我们定义的工具来处理用户的输入,并返回归属地和天气信息。
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
# 配置LLM
llm_cfg = {
'model': 'qwen',#这里可以根据自己的大模型类型修改配置参数
'model_server': 'http://localhost:11434/v1',#这里可以根据自己的大模型类型修改配置参数
'generate_cfg': {'top_p': 0.8}
}
# 创建agent
system_instruction = '你扮演一个助手,会调用工具,首先获取用户输入的手机号码,并调用手机号归属地查询服务工具获得城市地址,然后再调用天气查询工具获得所在城市的天气信息,最后进行整理,输出手机归属地和天气信息'
tools = ['get_mobile_address', 'get_weather']
bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg, system_message=system_instruction, description='function calling', function_list=tools)4.4创建聊天界面
我们将使用FastAPI来创建一个简单的Web界面,用户可以通过这个界面输入手机号,并获取归属地和天气信息。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Form
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates
app = FastAPI()
templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")
@app.get("/", response_class=HTMLResponse)
async def read_root(request: Request):
return templates.TemplateResponse("chat.html", {"request": request})
@app.post("/chat")
async def chat(message: str = Form(...)):
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': message}]
responses = bot.run(messages=messages)
return {"responses": [content['content'] for content in responses]}
# 运行FastAPI应用
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host='0.0.0.0', port=9000, workers=1)创建一个简单的html页面,如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Chat Interface</title>
<script>
function send_message() {
var message = document.getElementById("message").value;
if (message.trim() === "") {
alert("Message cannot be empty!");
return;
}
fetch("/chat", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
},
body: "message=" + encodeURIComponent(message),
})
.then(response => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Network response was not ok");
}
return response.json();
})
.then(data => {
var responses = data.responses;
var chat_window = document.getElementById("chat-window");
responses.forEach(response => {
var response_div = document.createElement("div");
response_div.innerText = response; // Fixed to access response directly
chat_window.appendChild(response_div);
});
document.getElementById("message").value = "";
chat_window.scrollTop = chat_window.scrollHeight;
})
.catch(error => console.error("Error:", error));
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chat-window" style="width: 80%; height: 400px; border: 1px solid #000; overflow-y: scroll;"></div>
<input type="text" id="message" placeholder="Type a message..." style="height: 100px;width: 80%;">
<button onclick="send_message()" style="background-color: blue; color: white; font-size: larger; padding: 10px 20px;">Send</button>
</body>
</html>五、小结
至此,我们实现了一个anget,他可以接收我们输入的电话号码,并且调用本地大模型进行处理,先是调用一个手机号码归属地查询tool,再去调用一个天气查询爬虫tool,最后大模型综合tool的反馈信息进行整合后输出给用户。以上是简单的实现,为了更加的准确好用需要进一步优化,包括qwen-anget本身好像有点问题,有时候只能调用一个手机号码归属地函数发挥不是很稳定因此需要优化prompt,第二,可以加入更多检查工具,比如,输入的号码检查,让大模型自己先检查一下对不对,比如对回答进行一些过滤,过滤掉不必要的信息等。
本文章转载微信公众号@机智新语
最新文章
- 如何获取百度语音翻译 API Key 密钥(分步指南)
- OpenAI OSS API 实战:打造智能客服与多轮对话系统全攻略
- eDRV的EV充电应用API:革新电动汽车即插即充体验
- 使用gin搭建api后台系统之框架搭建
- 什么是API定义?
- 不要让它们潜伏在暗处: 发现影子API的工具
- kfp-server-api:一个省时高效的 Python 库
- Postman API 自动化测试教程:入门指南及更多 – Nao
- 从2024年三个API趋势中学习,塑造新的一年
- 通过Fetch和Axios在React中使REST API
- 企业如何合法使用三方数据、自有的用户数据?
- 如何在 Python 和 Flask 中使用 IP API 查找地理位置?