使用NestJS和Prisma构建REST API:处理关系型数据
欢迎来到本教程,了解如何使用 NestJS、Prisma 和 PostgreSQL 构建 REST API! 在本教程中,您将学习如何在 NestJS REST API 中处理关系数据。
介绍
在本章中,我们将深入探讨如何在数据层和API层处理关系型数据。
- 首先,您将向数据库模式中添加
User模型,这个模型将包含与Article模型的一对多关系(即一个用户可以拥有多个文章)。 - 接下来,您将为
User端点实现API路由,以对User记录执行CRUD(创建、读取、更新和删除)操作。 - 最后,您将学习如何在API层中对
User-Article关系建模。
在本教程中,我们将基于第二章中构建的REST API进行操作。
开发环境
要学习本教程,您需要:
- …安装Node.js。
- …安装 Docker 和 Docker Compose。如果您使用的是 Linux,请确保您的 Docker 版本为 20.10.0 或更高版本。您可以通过在终端中运行
docker version来检查您的 Docker 版本。 - …安装 Prisma VS Code 扩展。这个扩展为Prisma提供了强大的IntelliSense功能和语法高亮显示,增强了开发体验。
- …可以选择访问 Unix shell(如 Linux 和 macOS 中的终端/shell)来运行本系列中提供的命令。
如果您没有 Unix shell(例如,您使用的是 Windows 计算机),您仍然可以继续操作,但可能需要为您的计算机修改 shell 命令。
克隆存储库
本教程的起始点位于GitHub仓库的end-validation分支。首先,您需要克隆该仓库并切换到end-validation分支。以下是操作步骤:
git clone -b end-validation git@github.com:prisma/blog-backend-rest-api-nestjs-prisma.git现在,执行以下操作以开始使用:
- 导航到克隆的目录:
cd blog-backend-rest-api-nestjs-prisma- 安装依赖项:
npm install- 使用 Docker 启动 PostgreSQL 数据库:
docker-compose up -d- 应用数据库迁移:
npx prisma migrate dev- 启动项目:
npm run start:dev注意:在步骤4中,我们不仅会生成Prisma客户端,还会设置数据库的初始种子数据。
项目结构和文件
您克隆的存储库应具有以下结构:
median
├── node_modules
├── prisma
│ ├── migrations
│ ├── schema.prisma
│ └── seed.ts
├── src
│ ├── app.controller.spec.ts
│ ├── app.controller.ts
│ ├── app.module.ts
│ ├── app.service.ts
│ ├── main.ts
│ ├── articles
│ └── prisma
├── test
│ ├── app.e2e-spec.ts
│ └── jest-e2e.json
├── README.md
├── .env
├── docker-compose.yml
├── nest-cli.json
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
├── tsconfig.build.json
└── tsconfig.json请注意:您可能会发现,此文件夹中还包含了一个名为test的目录。本教程中不会涉及对这部分内容的测试。
此存储库中的关键文件和目录如下:
src目录包含应用程序的源代码。它包含以下三个模块:- App 模块:位于
src目录的根部,是应用程序的入口点。它负责启动 Web 服务器。 - Prisma 模块:包含 Prisma Client,这是您与数据库的接口。
- Articles 模块:定义了
/articles路由的端点以及相关的业务逻辑。
- App 模块:位于
prisma文件夹包含以下内容:schema.prisma文件:定义了数据库架构。migrations目录:包含了数据库的迁移历史记录。seed.ts文件:包含一个脚本,用于使用虚拟数据为您的开发数据库填充初始数据。
docker-compose.yml文件:定义了您的 PostgreSQL 数据库的 Docker 映像。.env文件:包含了您的 PostgreSQL 数据库的数据库连接字符串。
将User模型添加到数据库
目前,您的数据库架构中仅包含一个模型:Article。文章可以由注册用户撰写。因此,您将在数据库架构中添加一个User模型,以反映这种关系。
首先更新 Prisma 架构:
// prisma/schema.prisma
model Article {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String @unique
description String?
body String
published Boolean @default(false)
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt
author User? @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int?
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String?
email String @unique
password String
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt
articles Article[]
}User模型包含了一些您可能期待的字段,例如id、email、password等,并且与Article模型建立了一对多的关系。这意味着一个用户可以拥有多篇文章,但一篇文章只能有一个作者。为了简化设计,author关系是可选的,所以您也可以创建没有指定作者的文章。
现在,要将这些更改应用到数据库,请执行迁移命令:
npx prisma migrate dev --name "add-user-model"如果迁移成功运行,您应该会看到以下输出:
...
The following migration(s) have been created and applied from new schema changes:
migrations/
└─ 20230318100533_add_user_model/
└─ migration.sql
Your database is now in sync with your schema
...更新您的种子脚本
seed 脚本负责使用虚拟数据填充数据库。您将更新seed脚本以在数据库中创建一些用户。
打开 prisma/seed.ts 文件并更新如下:
async function main() {
// create two dummy users
const user1 = await prisma.user.upsert({
where: { email: 'sabin@adams.com' },
update: {},
create: {
email: 'sabin@adams.com',
name: 'Sabin Adams',
password: 'password-sabin',
},
});
const user2 = await prisma.user.upsert({
where: { email: 'alex@ruheni.com' },
update: {},
create: {
email: 'alex@ruheni.com',
name: 'Alex Ruheni',
password: 'password-alex',
},
});
// create three dummy articles
const post1 = await prisma.article.upsert({
where: { title: 'Prisma Adds Support for MongoDB' },
update: {
authorId: user1.id,
},
create: {
title: 'Prisma Adds Support for MongoDB',
body: 'Support for MongoDB has been one of the most requested features since the initial release of...',
description:
"We are excited to share that today's Prisma ORM release adds stable support for MongoDB!",
published: false,
authorId: user1.id,
},
});
const post2 = await prisma.article.upsert({
where: { title: "What's new in Prisma? (Q1/22)" },
update: {
authorId: user2.id,
},
create: {
title: "What's new in Prisma? (Q1/22)",
body: 'Our engineers have been working hard, issuing new releases with many improvements...',
description:
'Learn about everything in the Prisma ecosystem and community from January to March 2022.',
published: true,
authorId: user2.id,
},
});
const post3 = await prisma.article.upsert({
where: { title: 'Prisma Client Just Became a Lot More Flexible' },
update: {},
create: {
title: 'Prisma Client Just Became a Lot More Flexible',
body: 'Prisma Client extensions provide a powerful new way to add functionality to Prisma in a type-safe manner...',
description:
'This article will explore various ways you can use Prisma Client extensions to add custom functionality to Prisma Client..',
published: true,
},
});
console.log({ user1, user2, post1, post2, post3 });
}种子脚本现在创建了两个用户和三篇文章。第一篇文章的作者是第一个用户,第二篇文章的作者是第二个用户,而第三篇文章则没有指定作者。
注意:目前,密码是以纯文本形式存储的。在实际应用中,您绝不应该这样做。在下一章中,您将了解到如何对密码进行加盐和哈希处理的更多信息。
要执行种子脚本,请运行以下命令:
npx prisma db seed如果种子脚本成功运行,您应该会看到以下输出:
...🌱 The seed command has been executed.在ArticleEntity中添加一个新的authorld字段
在迁移之后,您可能已经注意到出现了一个新的 TypeScript 错误。ArticleEntity 类实现了由 Prisma 生成的 Article 类型。Article 类型现在有了一个新的 authorId 字段,但是 ArticleEntity 类中还没有定义这个字段。TypeScript 识别到了类型之间的这种不匹配,并抛出了一个错误。您将通过在 ArticleEntity 类中添加 authorId 字段来解决这个错误。
在 ArticleEntity 中添加一个新的 authorId 字段:
// src/articles/entities/article.entity.ts
import { Article } from '@prisma/client';
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
export class ArticleEntity implements Article {
@ApiProperty()
id: number;
@ApiProperty()
title: string;
@ApiProperty({ required: false, nullable: true })
description: string | null;
@ApiProperty()
body: string;
@ApiProperty()
published: boolean;
@ApiProperty()
createdAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
updatedAt: Date;
@ApiProperty({ required: false, nullable: true })
authorId: number | null;
}在像JavaScript这样的弱类型语言中,开发者需要自行识别和修复类型相关的问题。而拥有像TypeScript这样的强类型语言的一大优势在于,它能够迅速帮助开发者发现并解决类型不匹配的问题。
为用户实现 CRUD 端点
在本部分中,我们将为REST API添加 /users 资源,这将赋予您对数据库中用户执行创建(Create)、读取(Read)、更新(Update)和删除(Delete)操作(即CRUD操作)的能力。
生成新的 user REST 资源
要为 users 生成新的REST资源,请运行以下命令:
npx nest generate resource您将会看到一些命令行提示(CLI prompts)。请根据提示相应回答问题:
- 您想为这个资源使用什么名称(复数形式,例如“users”)? users
- 您使用什么传输层? REST API
- 您是否需要生成CRUD入口点? 是
现在,您应该在src/users目录中找到一个新的用户模块,其中包含您REST端点所需的所有样板代码。
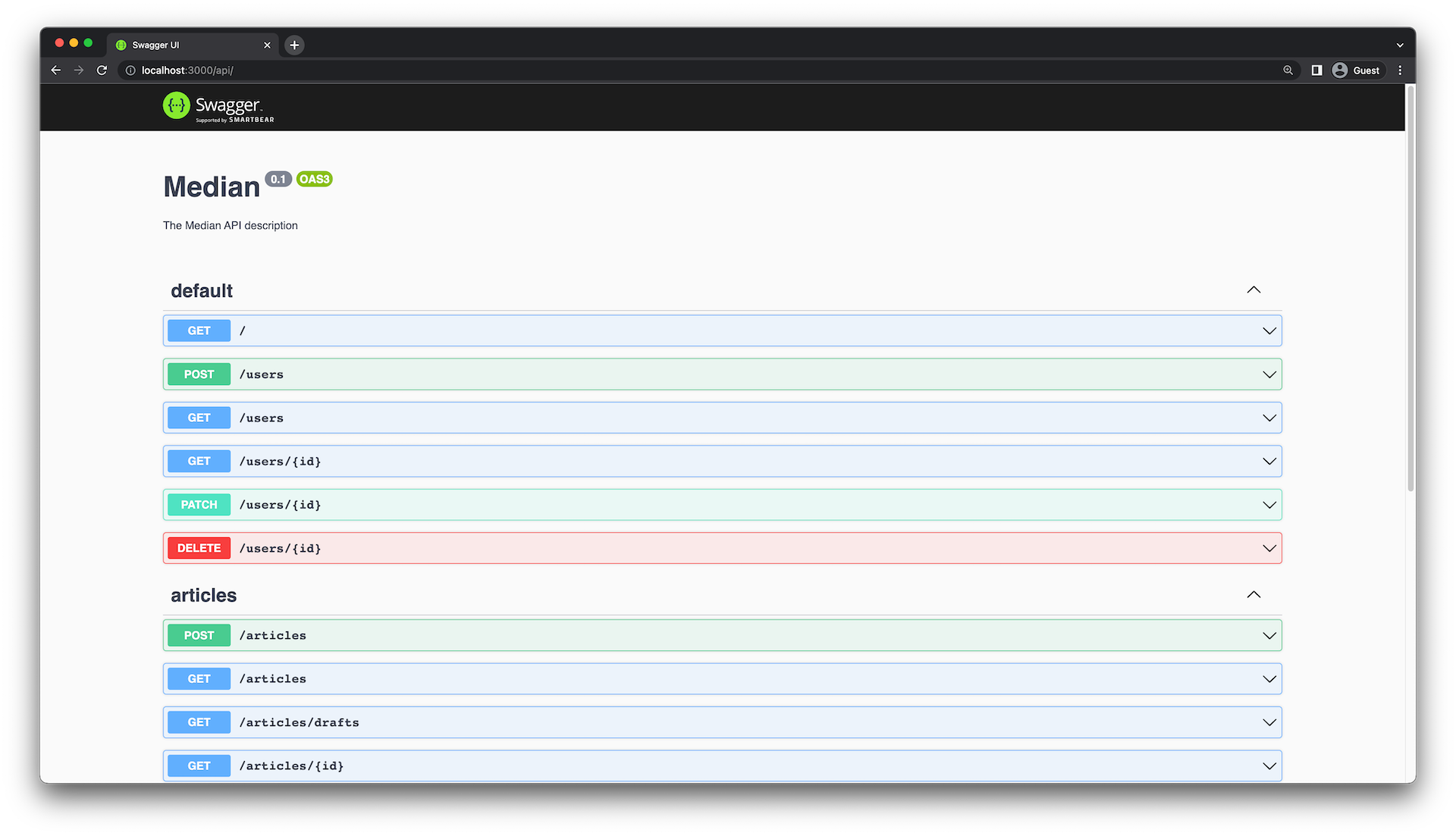
在src/users/users.controller.ts文件中,您会看到不同路由(也称为路由处理程序)的定义。处理每个请求的业务逻辑被封装在src/users/users.service.ts文件中。
如果您打开Swagger生成的API页面,您应该会看到类似这样的内容:
将 PrismaClient 添加到 Users 模块
要在 Users 模块内部访问 PrismaClient,您必须将 PrismaModule 作为导入项。请在 UsersModule 中添加以下导入内容:
// src/users/users.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UsersService } from './users.service';
import { UsersController } from './users.controller';
import { PrismaModule } from 'src/prisma/prisma.module';
@Module({
controllers: [UsersController],
providers: [UsersService],
imports: [PrismaModule],
})
export class UsersModule {}现在,您可以在 UsersService 中注入 PrismaService,并使用它来访问数据库。为此,请在 users.service.ts 文件中添加一个构造函数,如下所示:
// src/users/users.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
import { PrismaService } from 'src/prisma/prisma.service';
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
constructor(private prisma: PrismaService) {}
// CRUD operations
}定义User 实体和 DTO 类
与 ArticleEntity 类似,您将定义一个 UserEntity 类,用于在API层表示User实体。请在 user.entity.ts 文件中定义 UserEntity 类,如下所示:
// src/users/entities/user.entity.ts
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { User } from '@prisma/client';
export class UserEntity implements User {
@ApiProperty()
id: number;
@ApiProperty()
createdAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
updatedAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
name: string;
@ApiProperty()
email: string;
password: string;
}@ApiProperty 装饰器用于使属性在Swagger中可见。请注意,您没有为password字段添加@ApiProperty装饰器。这是因为该字段是敏感的,您不希望它在API中暴露。
注意:省略
@ApiProperty装饰器只会从Swagger文档中隐藏password属性。该属性仍然会在响应体中可见。您将在后面的部分处理这个问题。
DTO(数据传输对象)是一个定义数据如何通过网络发送的对象。您需要实现CreateUserDto和UpdateUserDto类,以分别定义在创建和更新用户时发送到API的数据。请在create-user.dto.ts文件中定义CreateUserDto 类,如下所示:
// src/users/dto/create-user.dto.ts
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { IsNotEmpty, IsString, MinLength } from 'class-validator';
export class CreateUserDto {
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty()
@ApiProperty()
name: string;
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty()
@ApiProperty()
email: string;
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty()
@MinLength(6)
@ApiProperty()
password: string;
}@IsString、@MinLength 和 @IsNotEmpty 是用于验证发送到API的数据的验证装饰器
UpdateUserDto 的定义会自动从 CreateUserDto 的定义中推断出来,因此无需显式定义。
定义 UsersService 类
UsersService 负责使用 Prisma Client 从数据库中修改和获取数据,并将其提供给 UsersController。您将在该类中实现 create()、findAll()、findOne()、update() 和 remove() 方法。
// src/users/users.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
import { PrismaService } from 'src/prisma/prisma.service';
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
constructor(private prisma: PrismaService) {}
create(createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return this.prisma.user.create({ data: createUserDto });
}
findAll() {
return this.prisma.user.findMany();
}
findOne(id: number) {
return this.prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { id } });
}
update(id: number, updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto) {
return this.prisma.user.update({ where: { id }, data: updateUserDto });
}
remove(id: number) {
return this.prisma.user.delete({ where: { id } });
}
}定义 UsersController 类
UsersController 负责处理对 users 端点的请求和响应。它将利用 UsersService 来访问数据库,使用 UserEntity 来定义响应体,以及使用 CreateUserDto 和 UpdateUserDto 来定义请求体。
控制器由不同的路由处理程序组成。您将在该类中实现五个路由处理程序,它们分别对应于五个端点:
create()–POST /usersfindAll()–GET /usersfindOne()–GET /users/:idupdate()–PATCH /users/:idremove()–DELETE /users/:id
在 users.controller.ts 文件中更新这些路由处理程序的实现,如下所示:
// src/users/users.controller.ts
import {
Controller,
Get,
Post,
Body,
Patch,
Param,
Delete,
ParseIntPipe,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { UsersService } from './users.service';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
import { ApiCreatedResponse, ApiOkResponse, ApiTags } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { UserEntity } from './entities/user.entity';
@Controller('users')
@ApiTags('users')
export class UsersController {
constructor(private readonly usersService: UsersService) {}
@Post()
@ApiCreatedResponse({ type: UserEntity })
create(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return this.usersService.create(createUserDto);
}
@Get()
@ApiOkResponse({ type: UserEntity, isArray: true })
findAll() {
return this.usersService.findAll();
}
@Get(':id')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: UserEntity })
findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return this.usersService.findOne(id);
}
@Patch(':id')
@ApiCreatedResponse({ type: UserEntity })
update(
@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number,
@Body() updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto,
) {
return this.usersService.update(id, updateUserDto);
}
@Delete(':id')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: UserEntity })
remove(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return this.usersService.remove(id);
}
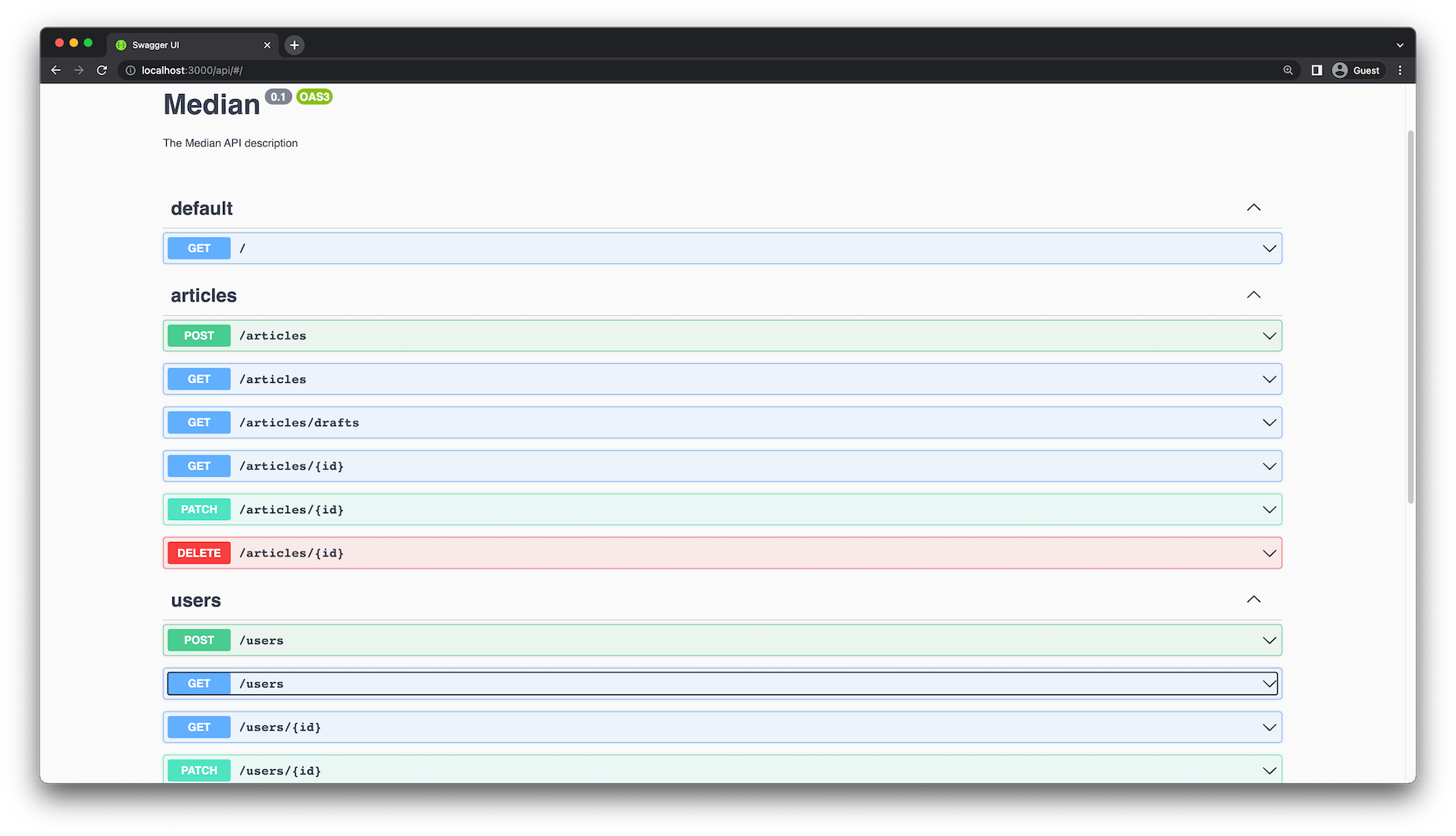
}更新后的控制器使用 @ApiTags 装饰器将端点分组到 users 标签下。它还使用 @ApiCreatedResponse 和 @ApiOkResponse 装饰器来定义每个端点的响应体。
更新后的Swagger API页面应该如下所示:
请随意测试不同的终端节点,以验证它们是否按预期运行。
从响应正文中排除 password字段
虽然 user API 按预期工作,但它存在一个重大的安全漏洞。不同端点的响应体中返回了password字段。
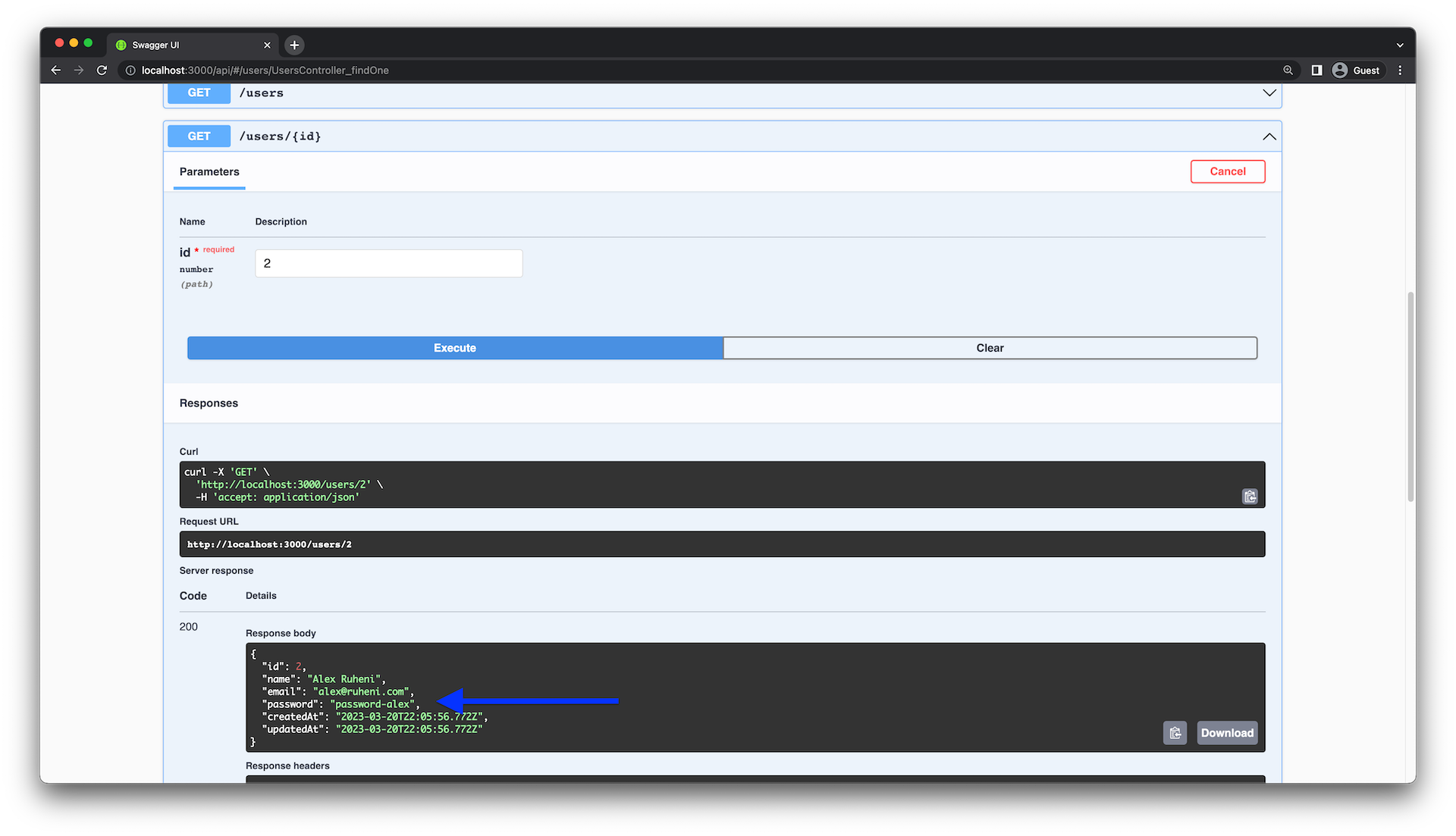
您有两种方法可以解决此问题:
- 从控制器的路由处理程序中手动从响应体中删除密码
- 使用拦截器自动从响应体中删除密码
第一种方法容易出错,并且会导致不必要的代码重复。因此,您将使用第二种方法。
使用ClassSerializerInterceptor从响应中移除字段
NestJS中的拦截器允许您挂钩到请求-响应周期,并在路由处理程序执行之前和之后执行额外的逻辑。在这种情况下,您将使用它来从响应体中删除 password 字段。
NestJS有一个内置的ClassSerializerInterceptor,可以用于转换对象。您将使用这个拦截器从响应对象中删除 password 字段。
首先,通过更新 main.ts 文件来全局启用ClassSerializerInterceptor:
// src/main.ts
import { NestFactory, Reflector } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { SwaggerModule, DocumentBuilder } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { ClassSerializerInterceptor, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe({ whitelist: true }));
app.useGlobalInterceptors(new ClassSerializerInterceptor(app.get(Reflector)));
const config = new DocumentBuilder()
.setTitle('Median')
.setDescription('The Median API description')
.setVersion('0.1')
.build();
const document = SwaggerModule.createDocument(app, config);
SwaggerModule.setup('api', app, document);
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();注意:您也可以将拦截器绑定到方法或控制器上,而不是全局绑定。
ClassSerializerInterceptor 使用 class-transformer 包来定义如何转换对象。在 UserEntity 类中使用 @Exclude() 装饰器来排除密码字段:
// src/users/entities/user.entity.ts
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { User } from '@prisma/client';
import { Exclude } from 'class-transformer';
export class UserEntity implements User {
@ApiProperty()
id: number;
@ApiProperty()
createdAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
updatedAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
name: string;
@ApiProperty()
email: string;
@Exclude()
password: string;
}如果您再次尝试使用GET /users/:id端点,您会发现密码字段仍然被公开🤔。这是因为目前控制器中的路由处理程序返回的是由Prisma Client生成的User类型。ClassSerializerInterceptor 仅适用于使用 @Exclude() 装饰器装饰的类。在这种情况下,它是 UserEntity 类。因此,您需要更新路由处理程序以返回 UserEntity 类型。
首先,您需要创建一个构造函数来实例化 UserEntity 对象。
// src/users/entities/user.entity.ts
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { User } from '@prisma/client';
import { Exclude } from 'class-transformer';
export class UserEntity implements User {
constructor(partial: Partial<UserEntity>) {
Object.assign(this, partial);
}
@ApiProperty()
id: number;
@ApiProperty()
createdAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
updatedAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
name: string;
@ApiProperty()
email: string;
@Exclude()
password: string;
}构造函数接收一个对象,并使用 Object.assign()方法将部分对象的属性复制到 UserEntity 实例中。partial 的类型是 Partial<UserEntity> ,这意味着部分对象可以包含UserEntity类中定义的任何属性子集。
接下来,更新 UsersController 的路由处理程序,使其返回 UserEntity 对象,而不是 Prisma.User 对象:
// src/users/users.controller.ts
@Controller('users')
@ApiTags('users')
export class UsersController {
constructor(private readonly usersService: UsersService) {}
@Post()
@ApiCreatedResponse({ type: UserEntity })
async create(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return new UserEntity(await this.usersService.create(createUserDto));
}
@Get()
@ApiOkResponse({ type: UserEntity, isArray: true })
async findAll() {
const users = await this.usersService.findAll();
return users.map((user) => new UserEntity(user));
}
@Get(':id')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: UserEntity })
async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return new UserEntity(await this.usersService.findOne(id));
}
@Patch(':id')
@ApiCreatedResponse({ type: UserEntity })
async update(
@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number,
@Body() updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto,
) {
return new UserEntity(await this.usersService.update(id, updateUserDto));
}
@Delete(':id')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: UserEntity })
async remove(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return new UserEntity(await this.usersService.remove(id));
}
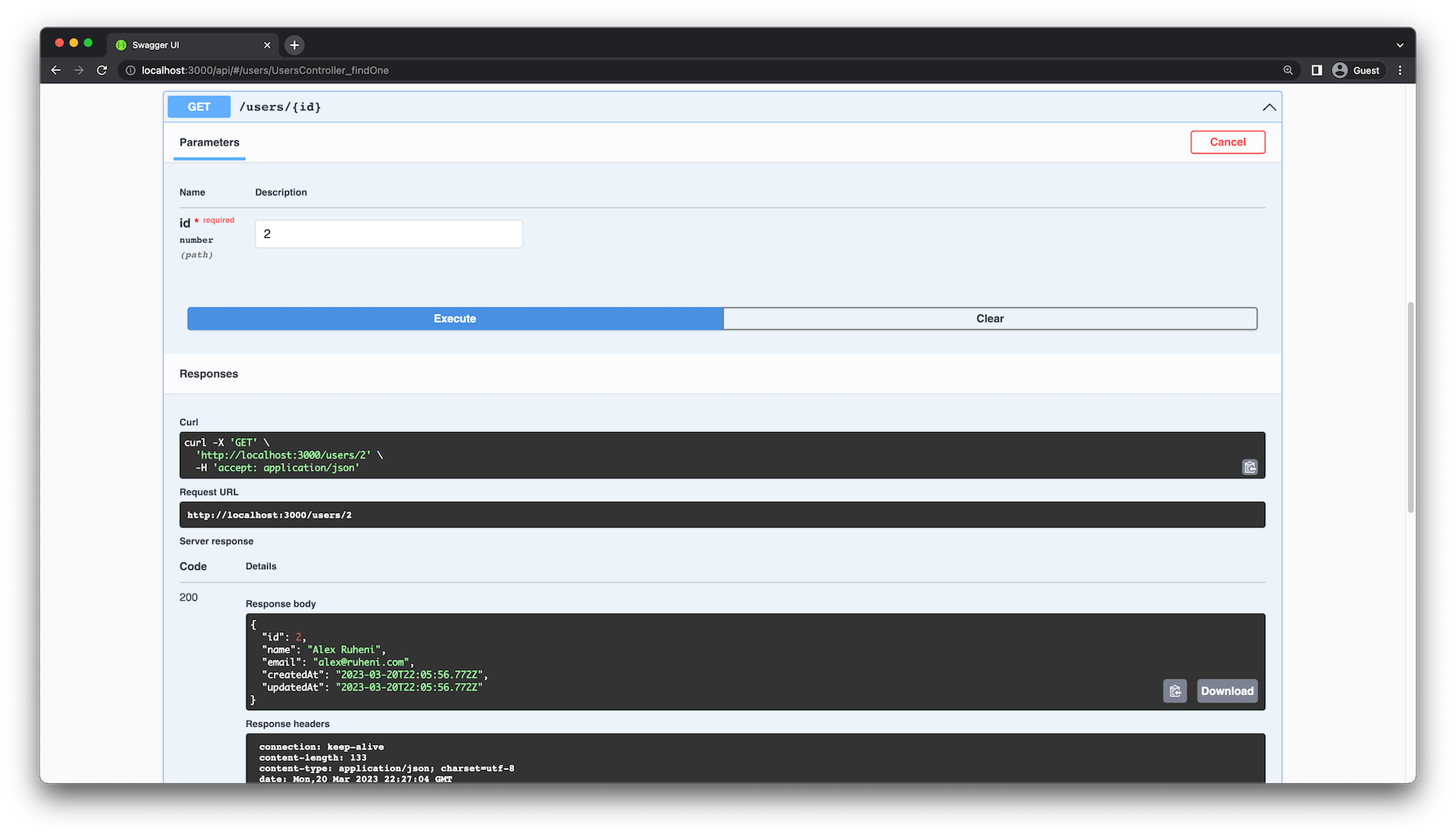
}现在,应该从 response 对象中省略 password。
返回文章及其作者
在第一章中,您实现了用于检索单篇文章的GET /articles/:id端点。目前,该端点仅返回文章的authorId,而不返回作者信息。为了获取作者信息,您需要向GET /users/:id端点发出额外的请求。如果您需要同时获取文章及其作者信息,这样做并不理想,因为您需要发出两个API请求。您可以通过在返回Article对象的同时返回作者信息来改进这一点。
数据访问逻辑是在ArticlesService中实现的。更新findOne()方法,以在返回Article对象的同时返回作者信息:
// src/articles/articles.service.ts
findOne(id: number) {
return this.prisma.article.findUnique({
where: { id },
include: {
author: true,
},
});
}如果您测试 GET /articles/:id 端点,您会发现如果文章有作者,那么作者信息会被包含在响应对象中。但是,有一个问题,password 字段将再次被暴露🤦。
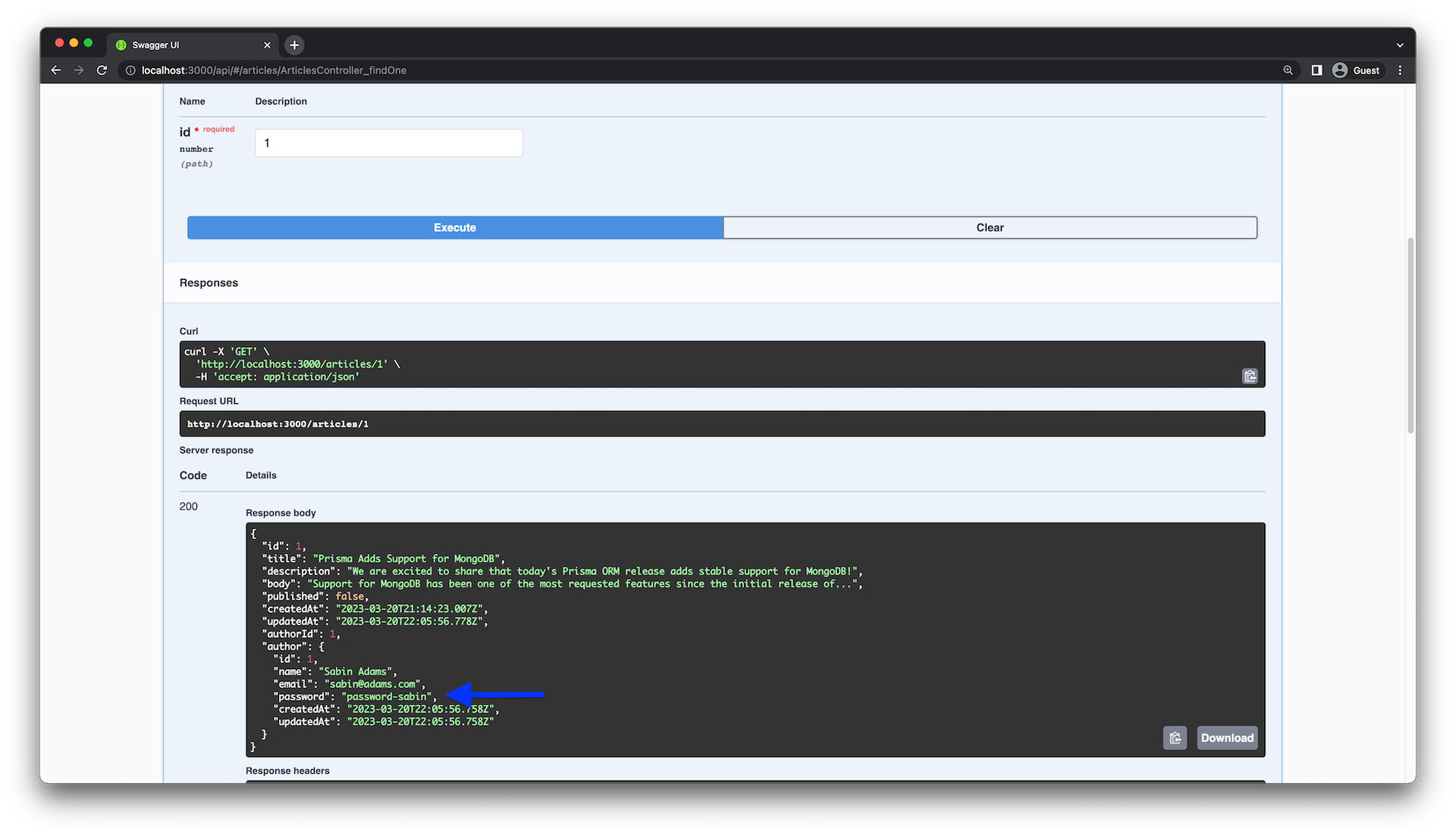
这个问题的原因与上次非常相似。目前,ArticlesController 返回的是由Prisma生成的类型实例,而 ClassSerializerInterceptor 是与 UserEntity 类一起工作的。为了解决这个问题,您将更新 ArticleEntity 类的实现,并确保它使用 UserEntity 的实例来初始化 author 属性。
// src/articles/entities/article.entity.ts
import { Article } from '@prisma/client';
import { ApiProperty } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { UserEntity } from 'src/users/entities/user.entity';
export class ArticleEntity implements Article {
@ApiProperty()
id: number;
@ApiProperty()
title: string;
@ApiProperty({ required: false, nullable: true })
description: string | null;
@ApiProperty()
body: string;
@ApiProperty()
published: boolean;
@ApiProperty()
createdAt: Date;
@ApiProperty()
updatedAt: Date;
@ApiProperty({ required: false, nullable: true })
authorId: number | null;
@ApiProperty({ required: false, type: UserEntity })
author?: UserEntity;
constructor({ author, ...data }: Partial<ArticleEntity>) {
Object.assign(this, data);
if (author) {
this.author = new UserEntity(author);
}
}
}您再次使用Object.assign()方法将数据对象的属性复制到ArticleEntity实例中。如果author属性存在,它将被初始化为UserEntity的实例。
现在,更新ArticlesController以返回ArticleEntity对象的实例:
// src/articles/articles.controller.ts
import {
Controller,
Get,
Post,
Body,
Patch,
Param,
Delete,
ParseIntPipe,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { ArticlesService } from './articles.service';
import { CreateArticleDto } from './dto/create-article.dto';
import { UpdateArticleDto } from './dto/update-article.dto';
import { ApiCreatedResponse, ApiOkResponse, ApiTags } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { ArticleEntity } from './entities/article.entity';
@Controller('articles')
@ApiTags('articles')
export class ArticlesController {
constructor(private readonly articlesService: ArticlesService) {}
@Post()
@ApiCreatedResponse({ type: ArticleEntity })
async create(@Body() createArticleDto: CreateArticleDto) {
return new ArticleEntity(
await this.articlesService.create(createArticleDto),
);
}
@Get()
@ApiOkResponse({ type: ArticleEntity, isArray: true })
async findAll() {
const articles = await this.articlesService.findAll();
return articles.map((article) => new ArticleEntity(article));
}
@Get('drafts')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: ArticleEntity, isArray: true })
async findDrafts() {
const drafts = await this.articlesService.findDrafts();
return drafts.map((draft) => new ArticleEntity(draft));
}
@Get(':id')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: ArticleEntity })
async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return new ArticleEntity(await this.articlesService.findOne(id));
}
@Patch(':id')
@ApiCreatedResponse({ type: ArticleEntity })
async update(
@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number,
@Body() updateArticleDto: UpdateArticleDto,
) {
return new ArticleEntity(
await this.articlesService.update(id, updateArticleDto),
);
}
@Delete(':id')
@ApiOkResponse({ type: ArticleEntity })
async remove(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return new ArticleEntity(await this.articlesService.remove(id));
}
}
现在,GET /articles/:id返回没有author字段的password对象:
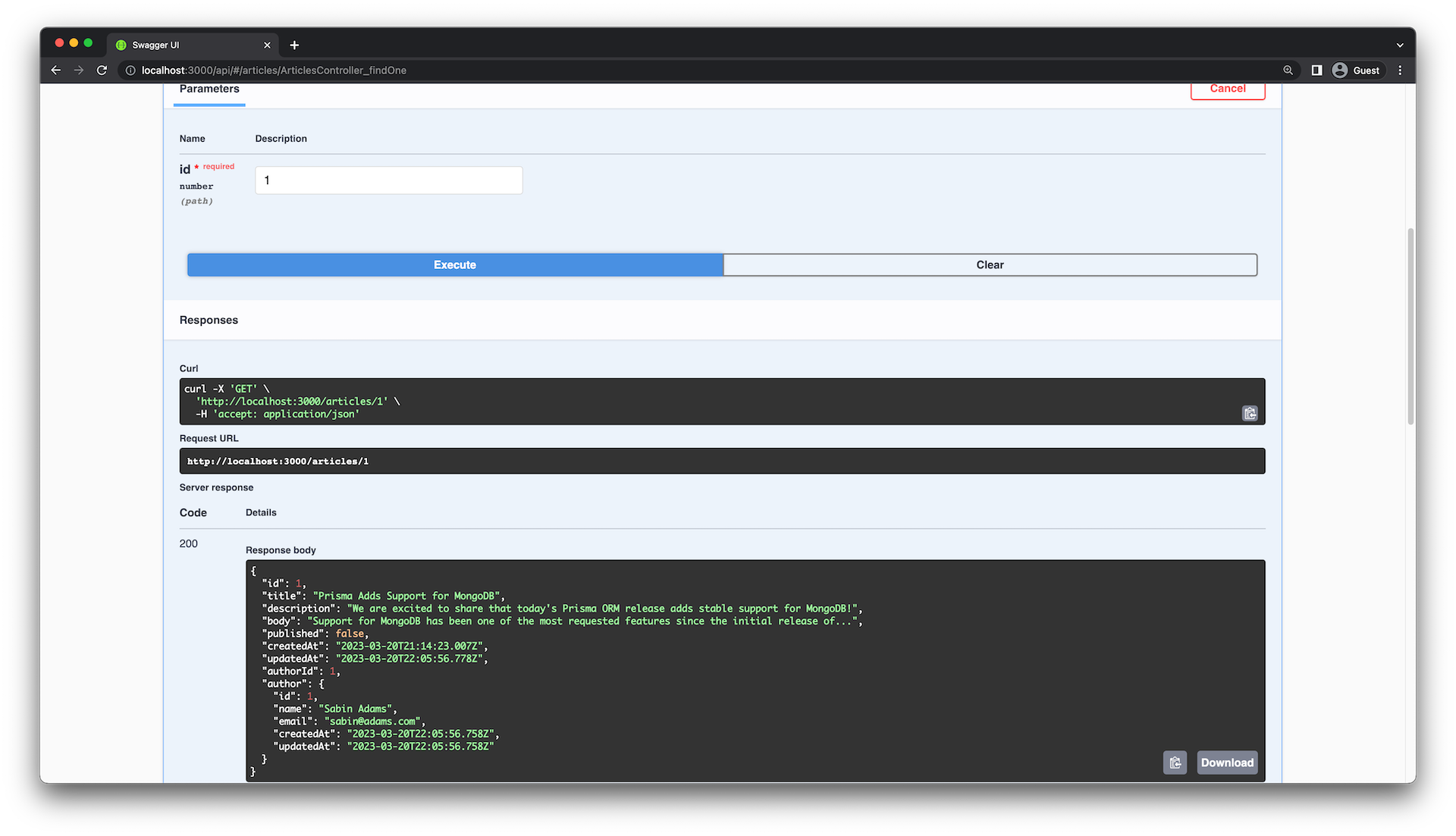
总结和结束语
在本章中,您学习了如何在NestJS应用程序中使用Prisma对关系型数据进行建模。您还了解了 ClassSerializerInterceptor 以及如何使用实体类来控制返回给客户端的数据。
您可以在GitHub仓库的 end-relational-data 分支中找到本教程的完整代码。如果您发现任何问题,请随时在仓库中提出问题或提交拉取请求(PR)。
原文链接:https://www.prisma.io/blog/nestjs-prisma-relational-data-7D056s1kOabc
热门API
- 1. AI文本生成
- 2. AI图片生成_文生图
- 3. AI图片生成_图生图
- 4. AI图像编辑
- 5. AI视频生成_文生视频
- 6. AI视频生成_图生视频
- 7. AI语音合成_文生语音
- 8. AI文本生成(中国)
最新文章
- 手把手教你用Python调用本地Ollama API
- 2025年提供LLM API的17家顶尖AI公司 – Apidog
- 如何使用 DeepSeek 构建 AI Agent:终极指南
- 如何获取Microsoft API Key 密钥实现bing搜索分步指南
- API和微服务:构筑现代软件架构的基石
- 如何免费调用高德经纬度定位API实现地理定位
- AI 驱动的 API 如何改变招聘:2024 年国内外顶级招聘相关API
- API治理:有效API管理的优秀实践和策略
- 企业 API 安全全解析:责任归属、最佳实践与 Boomi 控制平面管理
- WordPress: 从博客平台到AI驱动的内容管理巨人
- 2025 Mono 数据增强 API 使用指南|交易洞察与客户个性化服务实践
- 保险 APIs 应用:提升效率与客户体验